What Exactly Is Bitcoin and How Does It Work?

In the world of digital finance, few innovations have caused as much excitement — and confusion — as Bitcoin. Since its creation in 2009, Bitcoin has grown from an obscure tech experiment into a global financial revolution. It’s been praised as the “future of money” and criticized as a “bubble waiting to burst.”
But what exactly is Bitcoin? How does it work, and why do millions of people believe it could change the way we think about money forever?
Let’s break it down in simple, research-based terms.
What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, meaning it isn’t controlled by any government, bank, or corporation. It was invented in 2008 by an anonymous person (or group) using the name Satoshi Nakamoto, and officially launched in January 2009.
Unlike traditional money — which relies on central authorities like banks or governments — Bitcoin operates on a peer-to-peer network. This allows people to send and receive money directly without needing intermediaries.
In essence, Bitcoin is:
Digital (it exists only online — no physical coins or notes),
Decentralized (no central authority controls it),
Limited in supply (only 21 million bitcoins will ever exist), and
Transparent (every transaction is recorded publicly on a blockchain).
The Technology Behind Bitcoin: The Blockchain
The foundation of Bitcoin is a technology called blockchain — a distributed ledger that records every Bitcoin transaction ever made.
Think of blockchain as a digital notebook that everyone can read but no one can erase. It’s made up of “blocks” of data (transactions) linked together in chronological order, forming a “chain.”
Each block contains:
A list of verified transactions,
A timestamp, and
A cryptographic hash (a unique code linking it to the previous block).
Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes permanent and tamper-proof. This makes Bitcoin incredibly secure and transparent, since anyone can verify transactions — but no one can alter them.
How Bitcoin Transactions Work
Here’s how a typical Bitcoin transaction happens:
A user sends Bitcoin
Suppose Alice wants to send 0.1 BTC to Bob. She uses a digital wallet to initiate the transaction.Transaction verification
The transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network, where computers (called nodes) verify that Alice actually owns the Bitcoin she’s trying to send.Mining and block creation
Bitcoin transactions are grouped into blocks and verified by “miners.” These miners solve complex mathematical problems to confirm transactions — a process known as Proof of Work (PoW).Block added to blockchain
Once verified, the block is added to the blockchain. Bob’s wallet now shows 0.1 BTC, and Alice’s balance decreases accordingly.
This process typically takes 10 minutes per block and is the reason Bitcoin is considered one of the most secure payment networks in the world.
What Is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process of validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain.
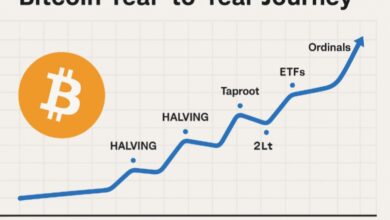
Miners use powerful computers to solve cryptographic puzzles. When a miner successfully solves one, they’re rewarded with new bitcoins — currently 6.25 BTC per block (this number halves approximately every four years in an event called the Bitcoin Halving).
Mining serves two crucial purposes:
It keeps the Bitcoin network secure.
It releases new bitcoins into circulation.
However, mining requires enormous computational power and electricity, leading to debates about its environmental impact. In response, newer blockchains (like Ethereum 2.0) have moved to more energy-efficient systems, but Bitcoin continues to rely on its traditional Proof of Work model.
Why Bitcoin Has Value
Bitcoin’s value isn’t backed by gold or government decree — it’s driven by scarcity, trust, and utility.
1. Limited Supply
Only 21 million bitcoins will ever exist. This scarcity mimics precious metals like gold and helps preserve value over time.
2. Decentralization
No government or bank can print more bitcoins or manipulate its supply — making it immune to inflationary policies.
3. Global Acceptance
Bitcoin can be sent across borders in minutes, without the need for banks or currency exchanges.
4. Trust in Blockchain
Because transactions are transparent and irreversible, users trust the Bitcoin network to maintain fairness and integrity.
Bitcoin as an Investment
Over the past decade, Bitcoin has emerged as a popular investment asset. Early adopters who bought Bitcoin at a few dollars have seen it soar to tens of thousands of dollars per coin.
Investors see Bitcoin as:
A store of value (“digital gold”),
A hedge against inflation, and
A speculative asset that could yield high returns.
However, Bitcoin’s price is also extremely volatile — it can swing by thousands of dollars in a single day. As such, it’s important for investors to understand the risks before buying.
The Risks and Challenges of Bitcoin
While Bitcoin offers many opportunities, it also faces significant challenges:
Volatility: Bitcoin’s price can fluctuate wildly, making it risky for short-term traders.
Regulation: Governments worldwide are still developing laws to regulate cryptocurrencies.
Security Risks: Although blockchain itself is secure, exchanges and wallets can be hacked.
Energy Use: Bitcoin mining consumes large amounts of electricity, raising environmental concerns.
Scams and Misuse: Like any financial innovation, Bitcoin can be exploited by scammers and criminals.
These challenges don’t necessarily spell doom for Bitcoin — but they highlight the need for careful regulation and responsible use.
How to Buy and Store Bitcoin
If you’re considering buying Bitcoin, here’s how to get started safely:
Choose a Trusted Exchange:
Popular platforms include Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken.Set Up a Wallet:
You’ll need a digital wallet to store your Bitcoin.Hot wallets are online and convenient but less secure.
Cold wallets (hardware or paper wallets) store Bitcoin offline for maximum safety.
Secure Your Private Keys:
Your private key is like the password to your Bitcoin. Never share it with anyone.Invest Wisely:
Only invest what you can afford to lose and diversify your portfolio.
The Future of Bitcoin
Bitcoin has already reshaped the financial landscape, inspiring thousands of cryptocurrencies and the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi).
Some experts predict that Bitcoin could become a mainstream global currency, while others believe it will remain a digital store of value like gold.
Either way, Bitcoin has proven that people around the world are ready for a new kind of money — one that’s transparent, borderless, and not controlled by any central power.
Conclusion
Bitcoin is more than just an internet currency — it’s a revolution in financial technology. By removing intermediaries, increasing transparency, and offering a decentralized system, Bitcoin has changed how we understand and use money.
However, as with any powerful innovation, it comes with risks. Price volatility, security threats, and regulatory uncertainty remain ongoing concerns.
Final Advice
If you’re new to Bitcoin, start with education. Understand how it works, store it securely, and avoid investing based solely on hype. Whether you see Bitcoin as a technological breakthrough or a speculative asset, one thing is clear: it has already left a permanent mark on the world economy.
The future of money might not be written on paper — it could be written on the blockchain.