How Does Cryptocurrency Work? A Beginner’s Guide to the Future of Money

In the past decade, cryptocurrency has evolved from a niche experiment into a global financial phenomenon. Whether it’s Bitcoin, Ethereum, or the thousands of digital currencies that followed, crypto has reshaped how we think about money, investment, and even privacy. But how does cryptocurrency actually work, and why has it attracted so much attention from investors, tech enthusiasts, and even governments?
This beginner’s guide will explain everything you need to know — from how cryptocurrencies function, to how you can safely use and invest in them.
What Is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a form of digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (like the U.S. dollar or euro), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks powered by blockchain technology — a distributed ledger maintained by computers (called nodes) around the world.
This means there’s no central authority like a bank or government controlling crypto. Instead, transactions are verified and recorded by the community through a consensus mechanism, ensuring transparency and security.
Popular examples of cryptocurrencies include:
Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, launched in 2009 by an anonymous creator, Satoshi Nakamoto.
Ethereum (ETH): Known for its smart contracts that allow developers to build decentralized applications (DApps).
Litecoin (LTC), Ripple (XRP), Solana (SOL), and Dogecoin (DOGE) — each designed for different purposes and use cases.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
To understand how crypto works, we need to look at three key components: blockchain, cryptography, and decentralization.
1. The Blockchain: A Digital Ledger
A blockchain is like a public, digital ledger that records every transaction made using a cryptocurrency. Imagine a shared Google Sheet that’s updated in real time, but instead of being hosted on one server, it’s stored across thousands of computers worldwide.
Each “block” contains:
A list of transactions
A timestamp
A unique code (called a hash) linking it to the previous block
Once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered — making the system tamper-resistant and highly secure.
2. Cryptography: Securing the System
Every transaction is encrypted using public-key cryptography.
Here’s how it works:
Each user has a public key (like an email address) and a private key (like a password).
When you send crypto, you use your private key to sign the transaction.
The network verifies your signature with your public key.
This ensures that only the rightful owner can spend their cryptocurrency, and all transactions are verified without revealing personal information.
3. Decentralization: Power to the People
Unlike traditional financial systems that rely on banks, cryptocurrencies operate on peer-to-peer (P2P) networks. This means users can send money directly to one another without needing intermediaries.
The decentralized nature of blockchain also makes it more resistant to censorship, fraud, and government interference.
How Are New Cryptocurrencies Created?
Most cryptocurrencies are created through a process called mining or staking.
Mining
Mining involves powerful computers solving complex mathematical problems to verify transactions and add them to the blockchain. In return, miners earn new coins as a reward.
Bitcoin, for example, uses a Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanism — but this requires significant electricity and computing power.
Staking
Newer cryptocurrencies like Ethereum 2.0 use Proof-of-Stake (PoS), where participants “stake” their coins to help validate transactions. It’s more energy-efficient and encourages long-term holding.
What Can You Do with Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency isn’t just for investment. Here are some practical uses:
Payments: Many companies, including Tesla and Microsoft (in the past), have accepted Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies as payment.
Remittances: Sending money across borders with lower fees compared to traditional banking systems.
Smart Contracts: Ethereum enables decentralized apps and contracts that execute automatically when conditions are met.
NFTs and Metaverse: Crypto powers new digital economies through non-fungible tokens and virtual worlds.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Users can borrow, lend, and earn interest without banks.
The Risks of Cryptocurrency
While crypto offers innovation, it also comes with risks:
Volatility: Prices can swing dramatically within hours.
Regulatory uncertainty: Governments are still developing policies for crypto.
Security threats: Hacks and scams can target exchanges and wallets.
Irreversible transactions: Once sent, crypto can’t be recalled if you make a mistake.
Before investing, it’s crucial to do thorough research, use reputable platforms, and secure your digital assets properly.
How to Get Started with Cryptocurrency
If you’re ready to explore crypto, here’s a simple roadmap:
Choose a Reliable Exchange:
Platforms like Coinbase, Binance, or Kraken allow you to buy and trade cryptocurrencies.Set Up a Wallet:
Use a hardware wallet (like Ledger or Trezor) for better security or a software wallet for convenience.Diversify Your Portfolio:
Don’t put all your money into one coin.Stay Informed:
Follow reputable news sources and understand market trends.Invest Responsibly:
Only invest what you can afford to lose — crypto is still a speculative asset.
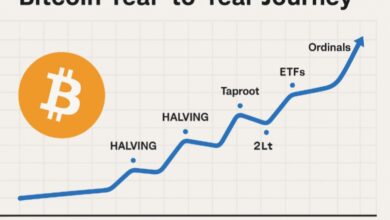
The Future of Cryptocurrency
As blockchain technology matures, cryptocurrencies are moving beyond speculation toward mainstream adoption.
Central banks are even exploring Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) inspired by crypto principles.
With growing acceptance, institutional investment, and technological innovation, crypto may redefine how global finance operates.
However, sustainability, regulation, and scalability will determine how successful this transformation will be.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency represents a revolution in how we perceive and use money. It offers freedom, transparency, and global accessibility — but it also demands responsibility, education, and awareness.
For beginners, the key is to learn before you leap. Understand how blockchain works, safeguard your assets, and start small. With careful strategy and informed decisions, crypto can become not just an investment opportunity, but a gateway to the future of digital finance.
Final Advice
If you’re curious about crypto, don’t be intimidated by the technology. Start with learning, experimenting with small amounts, and using trustworthy platforms. The world of cryptocurrency is still young — and those who understand its foundations today could benefit from its future potential tomorrow.